Understanding Microplastics: The Emerging Health Threat
Recent research has unveiled alarming findings regarding microplastics and their pervasive presence in both wildlife and human bodies. Over the past two decades, an in-depth analysis of approximately 7,000 studies has demonstrated that microplastics are not only widespread in the environment but are also increasingly entering our bodies through food and beverages. As reported by Science Magazine, the growing accumulation of these tiny plastic particles poses a significant health risk, likening it to a time bomb waiting to explode.
What are Microplastics?
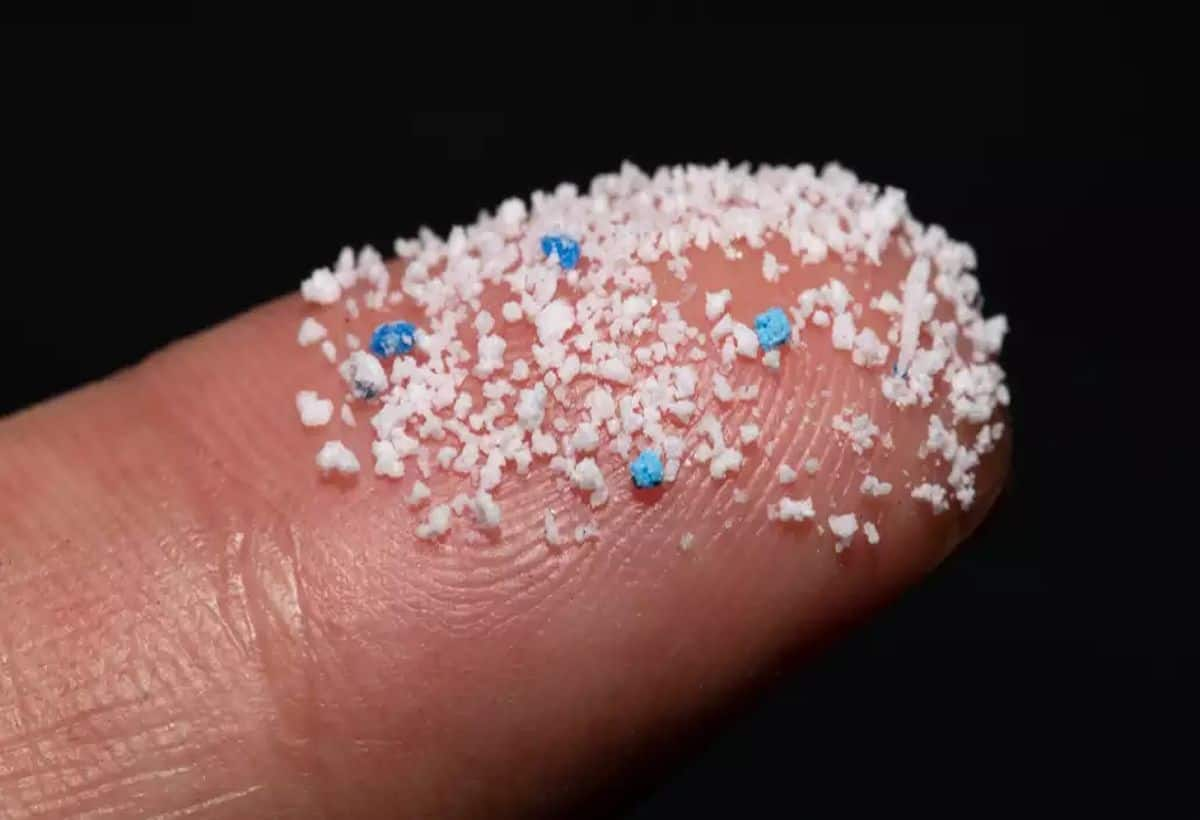
Microplastics are minuscule plastic fragments defined as particles less than 5 millimeters in length. It’s estimated that each person ingests between 12,000 to 1,000,000 microplastic particles annually, amounting to a total weight of around 7.7 grams to 287 grams per year. This alarming rate of ingestion is primarily attributed to various sources, as detailed in the following sections.
Sources of Microplastics
Microplastics can enter the human body through multiple avenues:
- Intentional Addition: Some products, such as facial scrubs and certain cosmetics, contain microbeads, which are a deliberate addition of microplastics.
- Unintentional Production: Microplastics are also produced when larger plastic items degrade. For instance, washing polyester garments releases tiny plastic fibers into the water supply, which can eventually reach the human food chain.
- Packing and Bottles: Everyday plastic items like bottles, bags, and packaging materials break down over time, contributing to microplastic pollution continuously.
The Global Picture of Plastic Pollution
A staggering 10,000 types of chemicals are blended into plastics without regulatory restrictions. Countries like China and Indonesia are leading contributors to global plastic pollution. The crisis is especially worrying in marine environments, where fish and other seafood are increasingly becoming carriers of microplastics, potentially transferring these harmful particles into the human food chain. It’s estimated that by 2050, the total weight of plastic in the ocean could surpass that of all fish combined.
Health Implications of Microplastics
The health repercussions of microplastic ingestion are still being studied, but emerging evidence suggests potential risks, including hormonal disruptions, inflammatory responses, and other unknown health issues due to the accumulation of these foreign particles in our bodies. As such, the issue is escalating into a public health concern that requires immediate attention.
Taking Action Against Microplastics
The primary culprit of microplastic proliferation is single-use plastic products. As of 2022, approximately 98 countries have partially or completely banned these items, a crucial step in reducing microplastic pollution. Lowering plastic consumption and promoting alternatives can significantly diminish environmental impact.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the increasing presence of microplastics in our ecosystems and bodies signifies a pressing health and environmental challenge. The scientific community urges immediate action to mitigate plastic pollution, including stricter regulations on plastic production and consumption, sustainability within industries, and public awareness campaigns. Understanding the sources and impacts of microplastics is crucial in safeguarding our health and environment for future generations.